Difference between Plant and Animal Cells
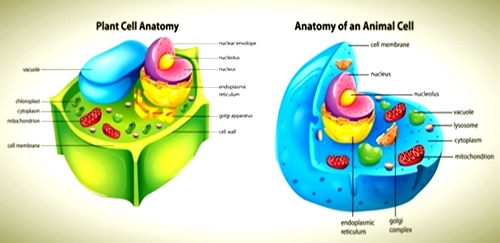
A cell is a vital support and functional unit of life. All life forms from primary bacterium to titan blue whale comprised of cells. The fundamental structure of both animal and plant cells are the same. The distinction in cell structure is essential because of the contrast in the method of nutrition. As plants are basically autotrophy and animals behave like heterotrophy.
Plant cells
Plant cells are also called eukaryotic cells, or cells with a film bound core. Dissimilar to prokaryotic cells, the DNA in a plant cell is accommodating inside of the essence. Notwithstanding having a core, plant cells likewise contain other layer bound organelles, or modest cell structures, that complete particular capacity vital for typical cell operation. Organelles have a wide variety of obligations that incorporate everything from creating hormones and chemicals to giving vitality to a plant cell.
Animal cells
Animal cells are also known as eukaryotic cells. Animal cells are having an outer limit known as the plasma film. A film bounds the core and the organelles of the cell. The hereditary material (DNA) in animal cells is inside of the core that is secured by a twofold layer. The cell organelles have an unfathomable scope of capacities to perform like hormone and chemical generation to giving vitality to the cells.
Plant cells VS Animal cells
The plant and animal cells have many similarities, as well as differences. In this article, we will discuss the main differences that exist between animal and plant cells.
-
Size:
Usually, the plant cells exist in large sizes.
Animal cells mostly exist in a smaller size as compared to the size of plant cells.
-
Cell wall:
A thick cell wall surrounds the plant cells as well as the plasma membrane is also there.
A flexible, thin plasma membrane bounds an animal cell. In animal cells, no cell wall is present.
-
Shape:
The plant cells have a rectangular fixed shape, which means they cannot transform their shape.
The animal cells are usually round in shape, and they have an irregular shape, which means they can transform their shape.
-
Plastids:
Plant cells are uncovered for sunlight to get chloroplast, so plastids exist in their cells.
In animal cells, plastids are not there.
-
Cilia:
Most of the plant cells do not contain cilia.
Cilia is present in animal cells.
-
Vacuoles:
A large central vacuole is present in mostly grown-up plant cells.
In animal cells, several small vacuoles are present.
-
Nucleus:
In-plant cells, the nucleus usually exists on one part in the peripheral cytoplasm.
In animal cells, the nucleus is present in the middle of the cell.
-
Centrioles:
In-plant cells, centrioles do not exist but present in moving cells that are there in lower plants.
In animal cells, centrioles are present.
-
Lysosomes:
In-plant cells, lysosomes are exceptional.
In animal cells, lysosomes are present.
-
Glyoxysomes:
Glyoxysomes are usually present in the plant cells.
However, it is absent in animal cells.
-
Tight junctions:
In-plant cells, desmosomes, and tight junctions are absent.
However, desmosomes and tight junctions are present in animal cells.
-
Food:
In-plant cells, the food which is reserved, that is usually in the form of starch.
In animal cells, reserved food is mostly present in the form of glycogen.
-
Plasmodesmata:
There is the presence of plasmodesmata in plant cells.
However, in animal cells, it is absent.
-
Synthesizes:
Plant cells have the power to synthesize the food they require, like coenzymes, amino acids, and vitamins.
However, animal cells have no power to synthesize the food they needed like coenzymes, all amino-acids, and vitamins.
-
Spindles formation:
When cell division occurs in plant cells, spindle formation is there in an astral.
In animal cells, when cell division is there, spindle formation is there in amphiastral.
-
Cytokinesis :
In-plant cells, cytokinesis is done by the method of the cell plate.
In animal cells, it occurs by constructing the furrowing.
-
Burst:
If we place plant cells in a hypotonic solution, the cell will not burst because of the presence of a cell wall.
Whereas when animal cells are in a hypotonic solution, the cell will burst as no cell wall is there.
-
Types of plant cells:
Following are the main types of plant cells:
Parenchyma– It is a simple cellular tissue found in the softer parts of plants such as ground tissue of stems, cortex of roots, mesophyll in leaves, etc. They help the plant to develop the bulk of the ground and also vascular tissues (xylem and phloem).
Sclerenchyma- It is composed of narrow, thick, and long cells, helps to make a plant stiff and strong. We can also call it a supporting (dead cell) tissue of plants. Sclerenchyma cells are divided into two types- sclereids and fibers. The cell wall of sclerenchyma is relatively thick, containing lignin. These cells vary significantly in their shapes and sizes.
Collenchyma- It is usually a dead cell containing a thick cell wall that provides structure and support to the plant body. It is often found in the epidermis, leaf veins, and outer layer of cells.
Water-conducting cells– A vascular tissue- xylem- is known as water-conducting cells as it transports the water from roots to all parts of the plants. It also gives physical support to plant.
-
Types of animal cells:
Following are the main types of plant cells:
Skin cells– These are the essential cells that cover up the bodies. It works as a barrier to the loss of water and protects the internal parts as well.
Muscle cells– These cells play an important role in the functioning of the body movement. It has three types: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth. They help in the protection of the organs.
Blood cells- They are divided into two types: white blood cells and red blood cells. The primary function they perform is to provide oxygen to all the body parts and collect carbon dioxide from them in return. These cells also carry vitamins, hormones, and enzymes to the parts of the body.
Nerve cells– nerve cells are the specialized cells, send information, or message electrochemically to the sensory receptors and CNS (Central Nervous System).
Bone cells– These cells help to maintain the body structure or skeleton of the animals. They play a role in the making of bones and help the body to move accordingly.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, we come to know that in some perspective, plant cells are more durable than animal cells, whereas, in some aspects, animal cells are stable.Do you agree with us?


It?s difficult to find well-informed people about this subject, but you seem like you know what you?re talking about!
Thanks
Yes you are right boy
You are right boy
You are right boy