Difference between Meiosis in Males and Females and Mitosis
Biological science is so advanced that it can inform about any of the things that are associated with the males and females. In both genders, the reproduction system is a very important process to consider and to talk about. Why it is important? It is mainly important because of the continuation of progeny. There are two types of methods are involved in it the first one is sexual and the second one is asexual by which plants and animals reproduce. This post will reveal the difference between Meiosis in Males and Females and Mitosis.
What is Meiosis in Males?
It deals with the reproduction process in which young ones are born from a single parent.
What is Meiosis in Females?
In this, the young ones are formed with the collaboration of both male and female parents. In this way, mitosis and meiosis are two major steps to generate which are of high importance to start up a new life.
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is a cell division or part of the cell cycle in which the division of the nucleus occurs. Two-parent nucleus replicates that results in two daughter cells. Both daughter cells have a similar number and type of chromosomes.
Meiosis in Males vs Meiosis in Females vs Mitosis:
What are they and what is the difference between them:
When it comes to meiosis, it is defined as a special type of reproduction that is mainly used by humans, animals, and certain plants. Now, here meiosis occurs in two different and opposite stages.
Meiosis 1
Meiosis 2
In human males, meiosis occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles while in females, it occurs in cells called oogonia.in males, it occurs at puberty, and in females, it generates right after the time of the birth. The retinoic acid that is formed by the primitive kidneys generate a step process of meiosis at the time of the birth. But in males, a tee is a condition which is opposite because it is suppressed till puberty by the tissues of the testis. This suppression can be overpowered if puberty and Sertoli cells start producing retinoic cells on their own. This step is of high importance in the whole process of meiosis in males and females.
Similarities of mitosis and meiosis:
Both mitosis and meiosis produce new cells, have similar basic steps and both process starts with a single parent cell.
While having similarities both mitosis and meiosis also differs in many ways such as:
- Mitosis occurs in all organisms (except viruses) while meiosis occurs in animals, plants, and fungi
- Mitosis helps to create body cells while meiosis helps to create sex cells
- There is one cell division in mitosis while in meiosis there are two cell divisions
- Mitosis produces diploid daughter cells while meiosis produces haploid daughter cells
- Mitosis produces 2 daughter cells while meiosis produces 4 daughter cell
- Daughter cells are identical in mitosis while in meiosis they are genetically different.
It’s process in males and females:
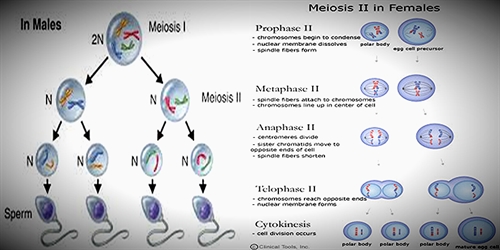
In meiosis 1, there is a splitting of gammets into two that there is a reduction in the two and also in the number of the chromosomes to half what is present in the main original cell. It is important to note that initially there is a crossing over the few of the chromosomes that are derived from each of the parents and in this process, half of the chromosomes get separated from each of the parent cells. In this way, all the chromosomes get equally distributed in two halves; and this is to be noted that thy carry the traits of their parent cells in equal portion. This step is also known as the reductional division. It is because those chromosomes reduce to half the number they are originally present before.
Here comes step next step that is meiosis 2, in this next stage there is an internal splitting of the daughter cells, and the four daughter cells with different permutation rose up and also with the combination of the chromosomes.
The process of mitosis consists of 5 steps:
Interphase – Prior to mitosis, each chromosome makes an exact copy of itself. The chromosomes then thicken and coil.
Prophase – It is divested into two:
In the early prophase, the centrioles, which have divided, form asters and move apart. The nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate.
In late prophase, the centrioles and asters are at opposite poles. The nucleolus and nuclear membrane have almost completely disappeared.
Metaphase – The doubled chromosomes and their centromeres attached to the spindle fibres which line up at mid-cell in metaphase.
Anaphase – Divided into two:
In early anaphase, the centromeres split. Half the chromosomes move to one pole, half to the other pole.
In late anaphase, the chromosomes have almost reached their respective poles. The cell membrane begins to pinch at the centre.
Telophase – The cell membrane completes constriction in telophase. Nuclear membranes form around the separated chromosomes.
When mitosis is completed there are 2 cells with the same type and number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Why it’s important:
Meiosis s important in mammals because in this process when male and female gametes fuse to form the zygote, then during this process there is a lost number of the chromosomes and they get replaced in this process in order to restore the original ones which were lost at that time of formation. The number of original chromosomes is total in the number of 42. If in the process of meiosis 1 or 2, there is a kind of error division. Then it would be called a dis junction process. It is important to note that it is an important process in reproduction.
Importance of mitosis:
Growth – Growth of an organism (production of new cells).
Repair – Repair of worn-out parts (healing of wounds)
The chromosome number doesn’t change
Growth and development of embryo
The recovery of damaged organs
Formation of all body cells
Mitosis is the basis for the asexual reproduction.
Conclusion:
Concluding the whole, Mitosis involves the division of body cells, while meiosis involves the division of sex cells. Meiosis is a process of cell replication where there is a reduction of the number of chromosomes to half from the original. It occurs at birth in females in oogonia but occurs at puberty in males in the seminiferous tubules.


This is extremely poorly written
what do u suggest to improve in it?
Instead of young ones, try “gametes”, you have also misspelled gametes as gamlets in one place.
“mitosis and meiosis are two major steps to generate which are of high importance to start up new life.” should be “mitosis and meiosis are two major steps to generate sex cells, which are important for new life”.
“What are they and what is the difference between them?” should be “What is it, and what are the differences between males and females?”
“When it comes to meiosis, it is defined as a special type of reproduction which is mainly used by humans, animals and certain plants.” should be “Meiosis is defined as a special type of reproduction which is mainly used by humans, animals and certain plants.”
“Now, here meiosis occurs in two different and opposite stages.” The first two words should go, as should the words “and opposite”.
“The retinoic acid that is formed by the primitive kidneys generatestep process of meiosis at the time of the birth” I think this should be “The retinoic acid that is formed by the primitive kidneys begins the process of meiosis at the time of birth.” but I cant really tell
“But in males, tee is a condition which is opposite because it is suppressed till puberty by the tissues of the testis.” This is unreadable
“This suppression can be overpowered if a puberty and sertoli cells start producing retinoic cells on their own.” Again, not sure, but I think this should be “This suppression can be overpowered if by puberty, or if sertoli cells start producing retinoic acid on their own. ”
“It’s process in males and females!: In meiosis 1, there is a splitting of gamlets into two that there is a reduction in the two and also in the number of the chromosomes to half what is present in the main original cell. It is important to note that initially there is a crossing over the few of the chromosomes that are derived from the each of the parent and in this process, half of the chromosomes gets separated from each of the parent cells. In this way, all the chromosomes gets equally distributed in two halves; and this is to be noted that thy carry the traits of their parent cells in equal portion. This step is also known as reductional division. It is because those chromosomes reduce to half the number they are originally present before.
Here comes step next step that is meiosis 2, in this next stage there is an internal splitting of the daughter cells and the four daughter cells with different permutation rose up and also with the combination of the chromosomes.”
This all needs to be completely rewritten. Try “The process in males and females: After meiosis 1, there are two daughter cells, each with 46 chromosomes (the standard number, or diploid number). Half of the chromosomes in each cell come from each parent. This is known as reductional division. In Meiosis 2, the chromosomes and cells split again, leading to four daughter cells, and 23 chromosomes in each, the haploid number.
“Why it’s important?:” you either mean “Why it is important”, or “Why is it important?”
“Meiosis s important in mammals because in this process when male and female gametes fuse to form the zygote , then during this process there is lost number of the chromosomes and they gets replaced in this process in order to restore the original ones which were lost at that time of formation. The number of original chromosomes is total in number of 42. If in the process of meiosis 1 or 2, there is a kind of error division. Then it would be called as dis junction process. It is important to note that it is an important process in reproduction.”
This part is not only grammatically incorrect, it is wrong. I cant tell if you are talking about crossing over, or non-disjunction, but neither of these explain what you seem to be trying to say. Neither does disjunction. Here is a better explanation.
“Meiosis is important because it produces sex cells with half the usual number of chromosomes, which is required for reproduction in most species.”
To clarify the previous terms, disjunction is when the chromosomes separate during meiosis or mitosis. Non-disjunction is when this does not occur correctly, and this can cause disease. Crossing over is when small parts of the maternal and paternal chromosomes swap over during meiosis 1.
“Concluding the whole, meiosis is a process of cell replication where there is a reduction of the number of chromosomes to half from the original. It occurs at birth in females in oogonia but occurs at puberty in males in the seminiferous tubles.” should be “To conclude, meiosis is a type of cell replication in which the number of chromosomes is reduced to that of half of a regular cell. It begins at birth in females, in the oogonia, and at puberty in males, in the seminiferous tubules”
Hope this helps!
Source: Doing a genetics degree and procrastinating revision.
We really appreciate your detailed comment and vision.
Jesus
why jesus?
I loved this writing
thanks for appreciation.
no bruh
perverts …